AWS API Gateway Tutorial Step 1
This feature uses delegation. By default, delegation is disabled for tenants without an add-on in use as of 8 June 2017. Legacy tenants who currently use an add-on that requires delegation may continue to use this feature. If delegation functionality is changed or removed from service at some point, customers who currently use it will be notified beforehand and given ample time to migrate. In addition, note that delegation does not support the use of custom domains so any features depending on it may not be fully functional alongside a custom domain.
Step 1 - Set up the Amazon API Gateway
After completing this step, you will have:- Set up Amazon API Gateway using AWS Lambda functions to execute your service logic that stores and retrieves pets from an Amazon DynamoDB table;
- Created two unauthenticated REST service methods for getting and updating a list of pets.
Step 1. Create the Amazon DynamoDB Table
In the Amazon DynamoDB Console, click on Create Table.
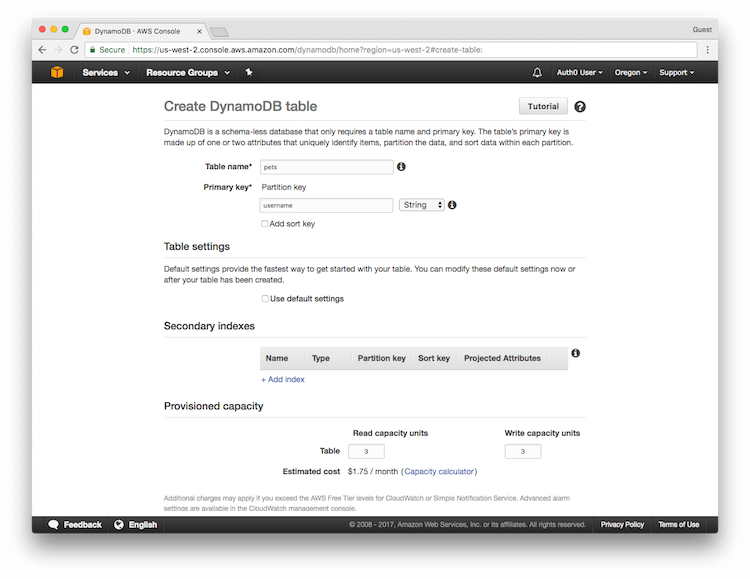
- Table name: Pets
- Primary key: username
- Primary key type: String
- Use default settings: unchecked
- Read capacity units: 3
- Write capacity units: 3
Step 2. Create the Policy that Grants AWS Lambda Functions Access to the DynamoDB Pets Table
Navigate to the AWS IAM Console. Click on Roles in the left menu, and then click the Create New Role button.
APIGatewayLambdaExecRole and click Next Step.
Select the Role Type. Under AWS Service Roles, select AWS Lambda.
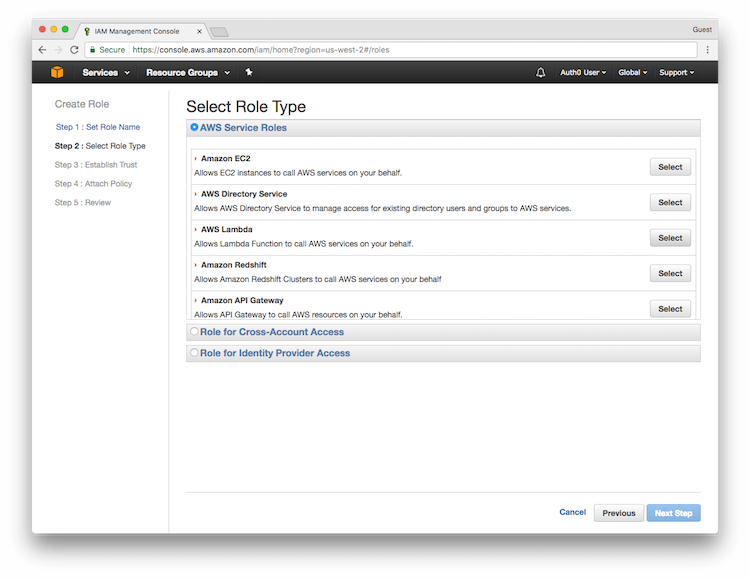
LogAndDynamoDBAccess and add the following code as the policy document (be sure to first update the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for your DynamoDB table). Click Apply Policy.
Step 2. Create the AWS Lambda Functions
The next three steps create the AWS Lambda functions for retrieving and updating pet information in the DynamoDB table.Create the Lambda Function for GetPetInfo
In the AWS Lambda Console, select Create a Lambda Function (if you have not created an AWS Lambda function before, you will click Get Started Now). On the Select blueprint screen, click Blank Function. You will then be prompted to Configure triggers. Click Next to proceed. You do not have to do so at this point. Finally, you will be asked to Configure function. Populate the appropriate fields with the following information:- Name:
GetPetInfo - Runtime: Node.js 6.10
{}) in the Execution Result section. The table is empty.
Create the Lambda Function for UpdatePetInfo
Repeat the instructions used to create theGetPetInfo function, but use the following instead as the function code:
{}).
Return to your GetPetInfo Lambda function and click Test again. You should now see a single pet.
Create the Third Lambda Function
You will create one additional Lambda function. While this function will do nothing, it is required by the OPTIONS method for CORS as described in a later section. Using the steps described above, create a Lambda function namedNoOp. The function’s code will be as follows:
Step 3. Create the Amazon API Gateway API
You will create an API with two methods: one willGET pet information, and one will POST pet information.
Method: GET Pet Information
Go to the Amazon API Gateway Console, and click Create API. If this is the first time you are creating an API, you will see a screen prompting you to Get Started instead. If this is the first time you are creating an API, you will be prompted to create an Example API. Click OK to exit the pop-up notification, and choose the New API radio button instead of the Example API button. Name the APISecurePets and click Create API.
Navigate to the Resources tab of the SecurePets API and click the Create Resource action.
Name the resource Pets and click Create Resource again.
In the left pane, select /pets and then click the CreateMethod button.
In the drop-down, select GET and click the checkmark button. Provide the following configuration values for the GET method:
- Integration type: Lambda Function;
- Lambda Region: Region you are located in;
- Lambda Function: GetPetInfo.
Method: POST Pet Information
Creating the API used toPOST pet information is similar to creating the one used to GET pet information.
In the left pane, select /pets, and click CreateMethod.
In the drop-down, select POST, and click the checkmark button.
Select Lambda Function for Integration Type, select the region you are located in, and select UpdatePetInfo for the Lambda function.
Click Save and then OK when prompted in the popup to grant permissions to the Lambda function.
Test, and paste the following for the request body:
{}).
Return to the GET method, and click Test again to see that the response body indicates there are two pets listed in the table:
Method: OPTIONS
Instead of creating a lambda function that performs no action, you can create anOPTIONS method on the API Gateway.
In the left pane, select /pets, and click CreateMethod. In the drop down, select OPTIONS, and click the checkmark button. Select Mock for Integration Type. Click Save.
Leaving the Response Body blank, click Test. You should receive a Response Body indicating no data.
At this point, the AWS Lambda functions and the Amazon API Gateway methods are defined with no security.
