Refresh Token Rotation
rotation is a technique for getting new using refresh tokens that goes beyond silent authentication. Refresh tokens are typically longer-lived and can be used to request new access tokens after the shorter-lived access tokens expire. Refresh tokens are often used in native applications on mobile devices in conjunction with short-lived access tokens to provide seamless UX without having to issue long-lived access tokens.
With enabled in the , every time an application exchanges a refresh token to get a new access token, a new refresh token is also returned. Therefore, you no longer have a long-lived refresh token that, if compromised, could provide illegitimate access to resources. As refresh tokens are continually exchanged and invalidated, the threat is reduced.
The way refresh token rotation works in Auth0 conforms with the OAuth 2.0 BCP and works with the following flows:
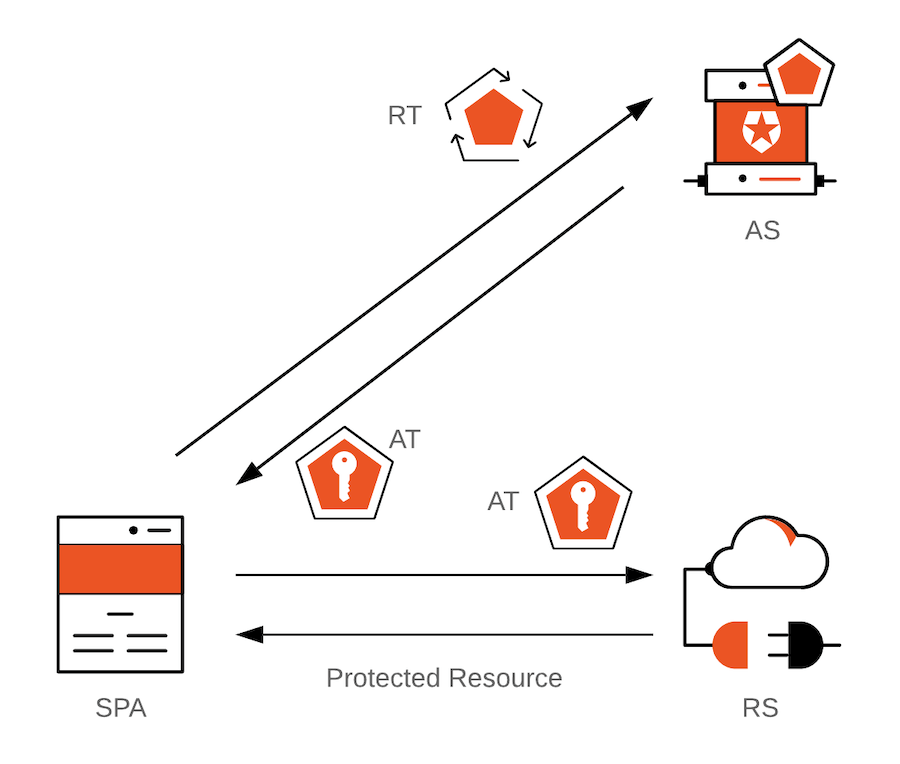 Unfortunately, long-lived refresh tokens are not suitable for SPAs because there is no persistent storage mechanism in a browser that can assure access by the intended application only. As there are vulnerabilities that can be exploited to obtain these high-value artifacts and grant malicious actors access to protected resources, using refresh tokens in SPAs has been strongly discouraged.
Refresh token rotation offers a remediation to end-user sessions being lost due to side-effects of browser privacy mechanisms. Because refresh token rotation does not rely on access to the Auth0 session cookie, it is not affected by ITP or similar mechanisms.
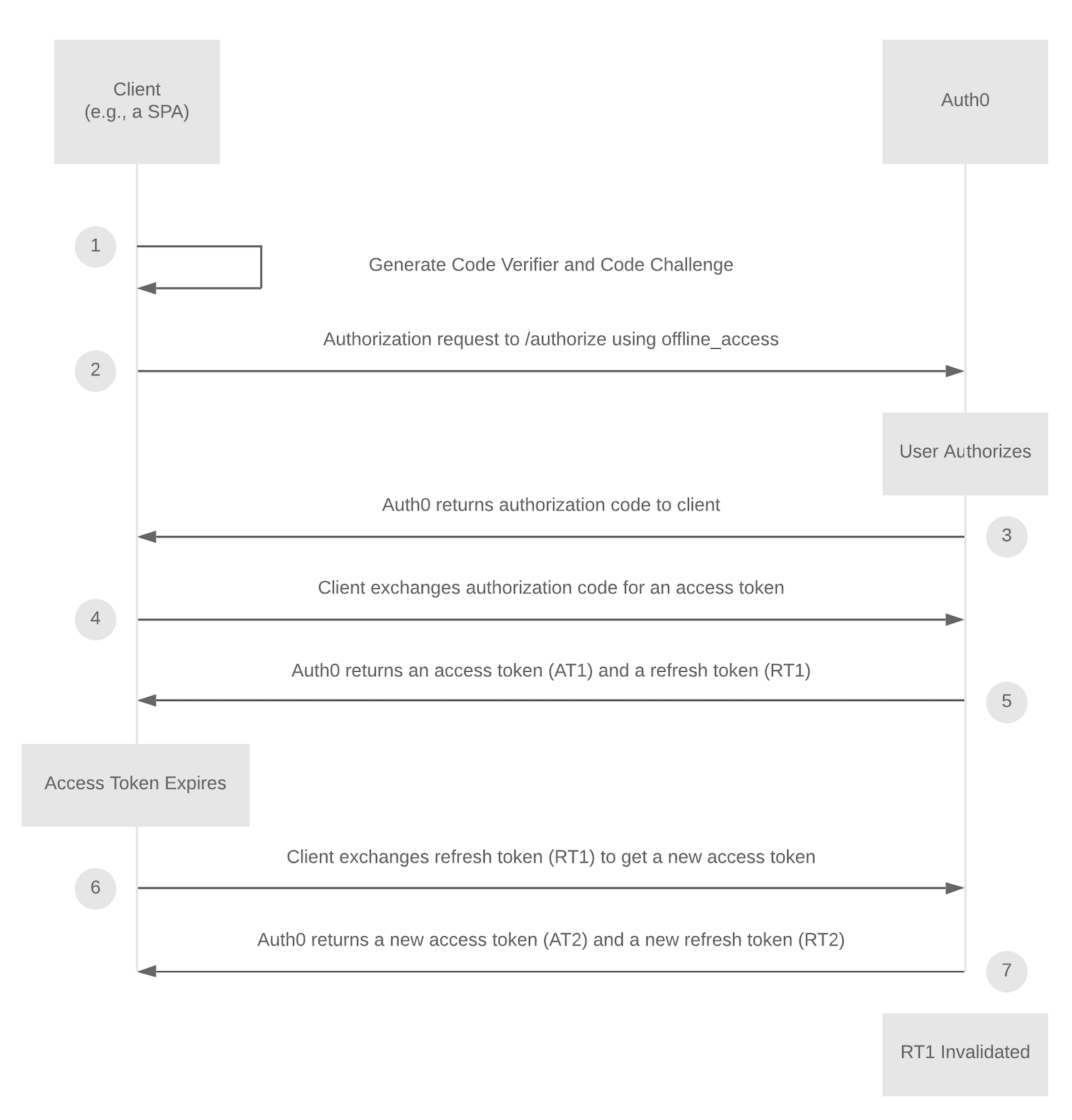
The following state diagram illustrates how refresh token rotation is used in conjunction with the Authorization Code Flow with PKCE, but the general principle of getting a new refresh token with each exchange applies to all supported flows.
Unfortunately, long-lived refresh tokens are not suitable for SPAs because there is no persistent storage mechanism in a browser that can assure access by the intended application only. As there are vulnerabilities that can be exploited to obtain these high-value artifacts and grant malicious actors access to protected resources, using refresh tokens in SPAs has been strongly discouraged.
Refresh token rotation offers a remediation to end-user sessions being lost due to side-effects of browser privacy mechanisms. Because refresh token rotation does not rely on access to the Auth0 session cookie, it is not affected by ITP or similar mechanisms.
The following state diagram illustrates how refresh token rotation is used in conjunction with the Authorization Code Flow with PKCE, but the general principle of getting a new refresh token with each exchange applies to all supported flows.
 This means you can safely use refresh tokens to mitigate the adverse effects of browser privacy tools and provide continuous access to end-users without disrupting the user experience.
This means you can safely use refresh tokens to mitigate the adverse effects of browser privacy tools and provide continuous access to end-users without disrupting the user experience.
- Authorization Code Flow
- Authorization Code Flow with Proof Key for Code Exchange
- Device Authorization Flow
- Resource Owner Password Flow
Maintain user sessions in SPAs
Until very recently, SPAs maintained the user’s session by using the Authorization Code Flow with PKCE in conjunction with silent authentication. Recent developments in browser privacy technology, such as Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) prevent access to the Auth0 , thereby requiring users to reauthenticate.

Automatic reuse detection
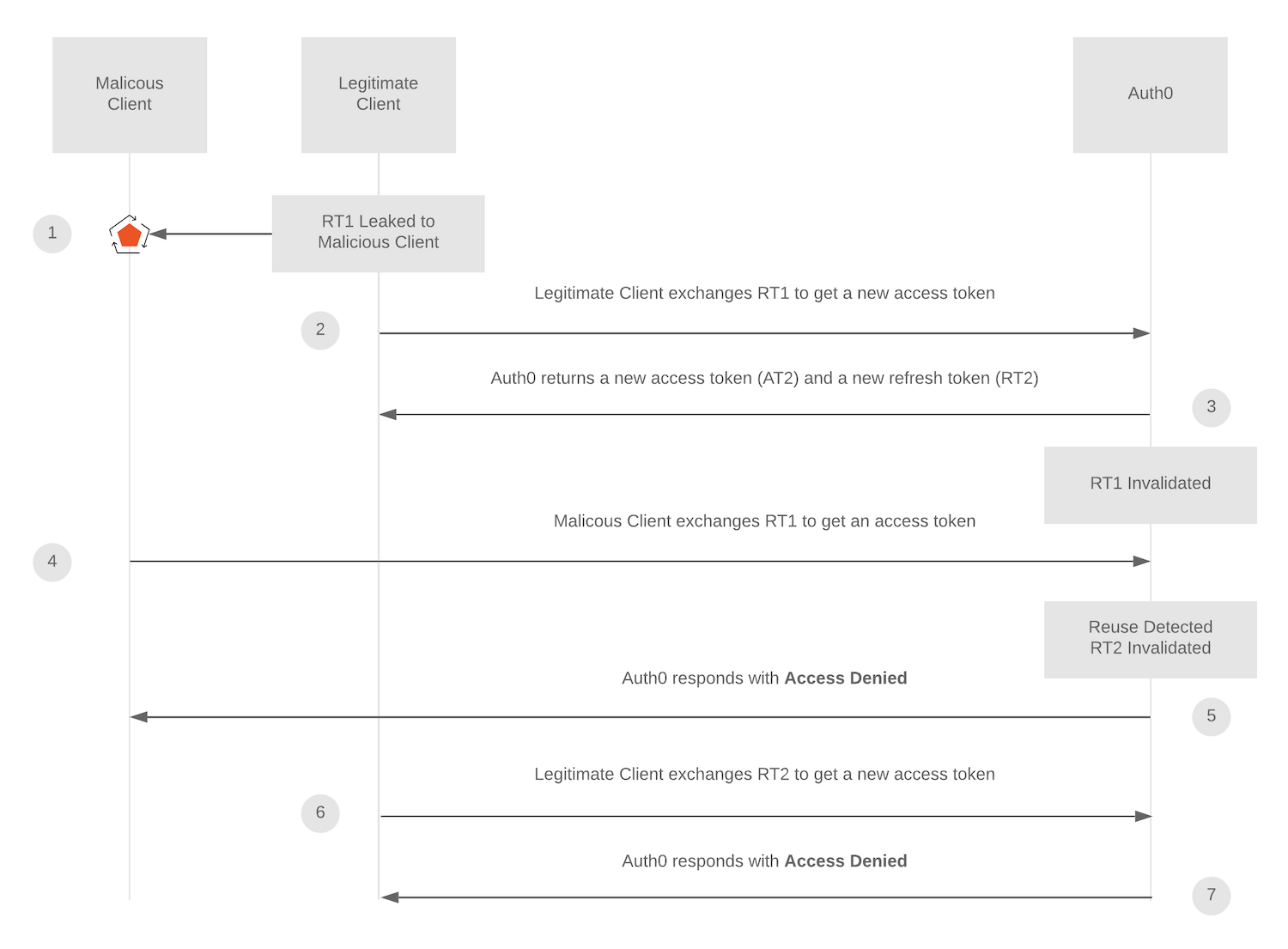
When a client needs a new access token, it sends the refresh token with the request to Auth0 to get a new token pair. As soon as the new pair is issued by Auth0, the refresh token used in the request is invalidated. This safeguards your app from replay attacks resulting from compromised tokens. Without enforcing sender-constraint, it’s impossible for the to know which actor is legitimate or malicious in the event of a replay attack. So it’s important that the most recently issued refresh token is also immediately invalidated when a previously-used refresh token (already invalidated) is sent to the authorization server. This prevents any refresh tokens in the same token family (all refresh tokens descending from the original refresh token issued for the client) from being used to get new access tokens. For example, consider the following scenario:
- Legitimate Client has refresh token 1, and it is leaked to or stolen by Malicious Client.
- Legitimate Client uses refresh token 1 to get a new refresh token/access token pair.
- Auth0 returns refresh token 2/access token 2.
- Malicious Client then attempts to use refresh token 1 to get an access token. Auth0 recognizes that refresh token 1 is being reused, and immediately invalidates the refresh token family, including refresh token 2.
- Auth0 returns an access denied response to Malicious Client.
- Access token 2 expires and Legitimate Client attempts to use refresh token 2 to request a new token pair. Auth0 returns an access denied response to Legitimate Client.
- Re-authentication is required.
ferrt indicating a failed exchange) in logs. This can be especially useful in conjunction with Auth0’s log streaming capabilities to detect suspicious activity.
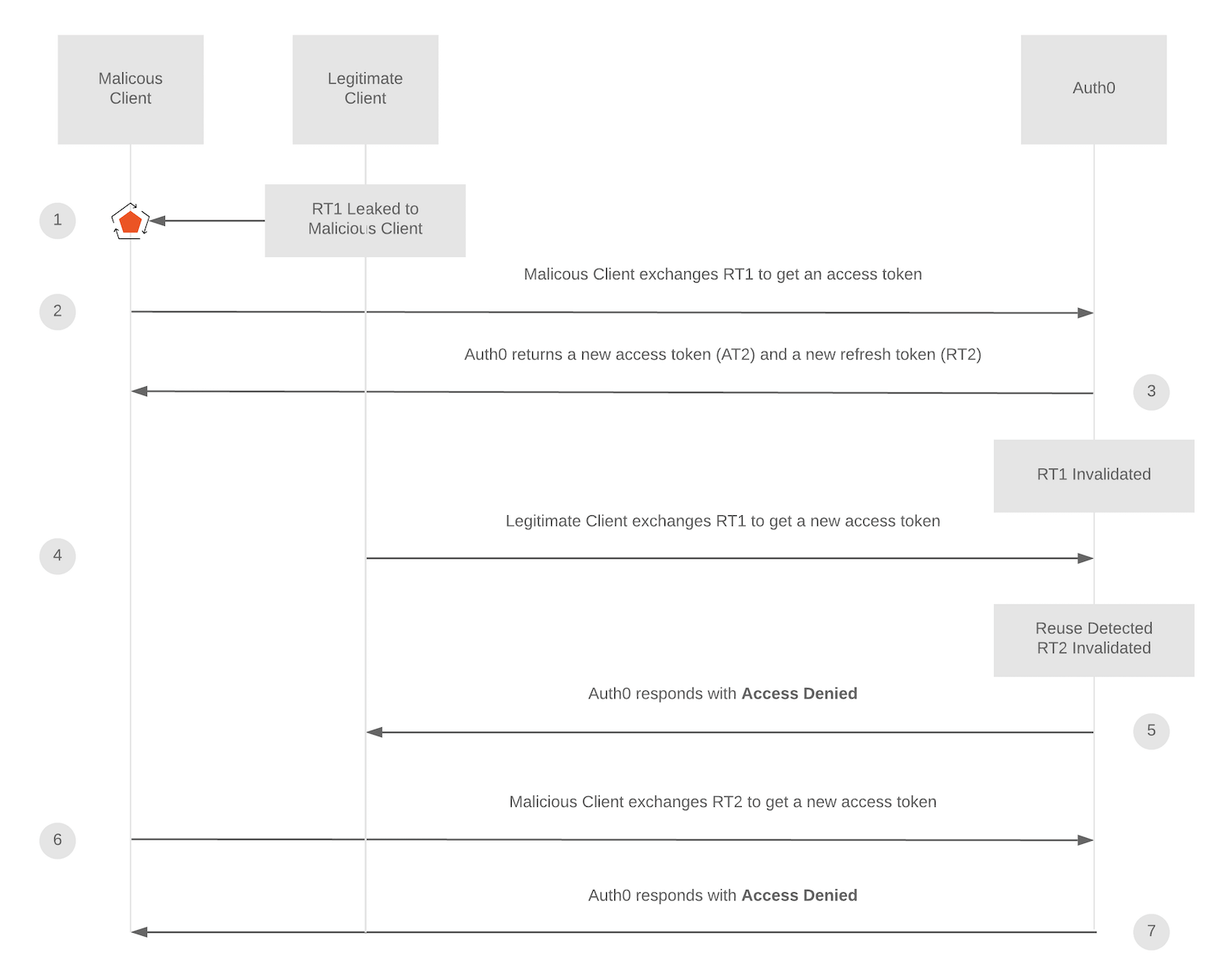
Another example is where the malicious client steals refresh token 1 and successfully uses it to acquire an access token before the legitimate client attempts to use refresh token 1. In this case, the malicious client’s access would be short-lived because refresh token 2 (or any subsequently issued refresh tokens) is automatically revoked when the legitimate client tries to use refresh token 1, as shown in the following diagram:

SDK support
The following SDKs include support for refresh token rotation and automatic reuse detection.- Auth0 SPA SDK
- Flutter (Web)
- Swift (iOS) SDK
- Android SDK
- Flutter
- React Native SDK
- WPF / Winforms
- Xamarin

